Key Capabilities of QES:
• Quality Management: Automate audits, manage non-conformances, and monitor quality metrics in real time.
• Process Efficiency: Eliminate bottlenecks, automate routine tasks, and enhance workflow integration.
• Compliance Tracking: Stay ahead of regulatory changes with advanced compliance management features.
• Data-Driven Insights: Leverage predictive analytics, customizable dashboards, and detailed reporting for better decision-making.
• Scalability and Flexibility: Adapt the platform to your specific business needs, with the ability to scale as your organization grows.
In essence, QES is designed to be more than just a tool—it’s a solution that integrates seamlessly into your business processes, driving improvements across the board. With QES, businesses can not only meet but exceed their operational goals, paving the way for sustained growth and success.
Handling Quality of Experience (QoE) Service (QES) capabilities involves managing and optimizing the performance and quality of service (QoS) metrics in networks and applications. To effectively handle QES capabilities, consider the following steps:
1. Understanding QES Capabilities • Quality of Service (QoS) Metrics: Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as latency, jitter, packet loss, throughput, and availability.
• Network Resource Management: Allocate bandwidth and prioritize traffic to maintain desired service quality.
• Monitoring Tools: Use tools to continuously monitor network performance and detect anomalies.
2. Implementing Quality of Service (QoS) Policies • Traffic Prioritization: Set up policies that prioritize critical traffic over less important traffic.
• Bandwidth Management: Allocate bandwidth based on the needs of different applications and users.
• Congestion Management: Use techniques like traffic shaping and load balancing to manage network congestion.
3. Performance Monitoring and Analysis
• Real-Time Monitoring: Use real-time monitoring tools to track network performance and identify potential issues.
• Data Analysis: Analyze collected data to understand performance trends and predict potential problems.
• Alerts and Notifications: Set up alerts to notify administrators of performance degradation or failures.
4. Optimization Techniques
• Adaptive Algorithms: Implement algorithms that adjust parameters dynamically based on current network conditions.
• Compression and Caching: Use compression and caching techniques to reduce bandwidth usage and improve response times.
• Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Utilize CDNs to distribute content closer to end-users, reducing latency and improving QoE.
5. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
• User Feedback: Collect feedback from users to understand their experience and identify areas for improvement.
• Continuous Testing: Regularly test network performance under different conditions to identify bottlenecks.
• Iteration: Continuously refine and improve QoS policies based on feedback and performance data.
6. Security Considerations
• Secure Data Transmission: Ensure data is encrypted and secure to protect the integrity and privacy of communications.
• DDoS Protection: Implement measures to protect against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which can degrade service quality.
7. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
• Adhere to Standards: Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements for quality of service.
• Reporting: Maintain accurate records of QoS metrics and report them as required by regulators or stakeholders.
The capabilities of QES (Quality and Efficiency Solution)
Benefits of Implementing QES
Implementing QES can provide several tangible benefits to an organization:
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes and automation reduce waste and increase productivity.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing resource use and reducing errors, QES helps lower operational costs.
- Improved Quality: Continuous monitoring and quality control ensure that products meet the highest standards.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Real-time data and analytics provide insights that support informed decision-making.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that operations adhere to industry regulations, reducing the risk of fines and legal issues.
- Greater Customer Satisfaction: Improved product quality and service lead to higher customer satisfaction and retention rates.
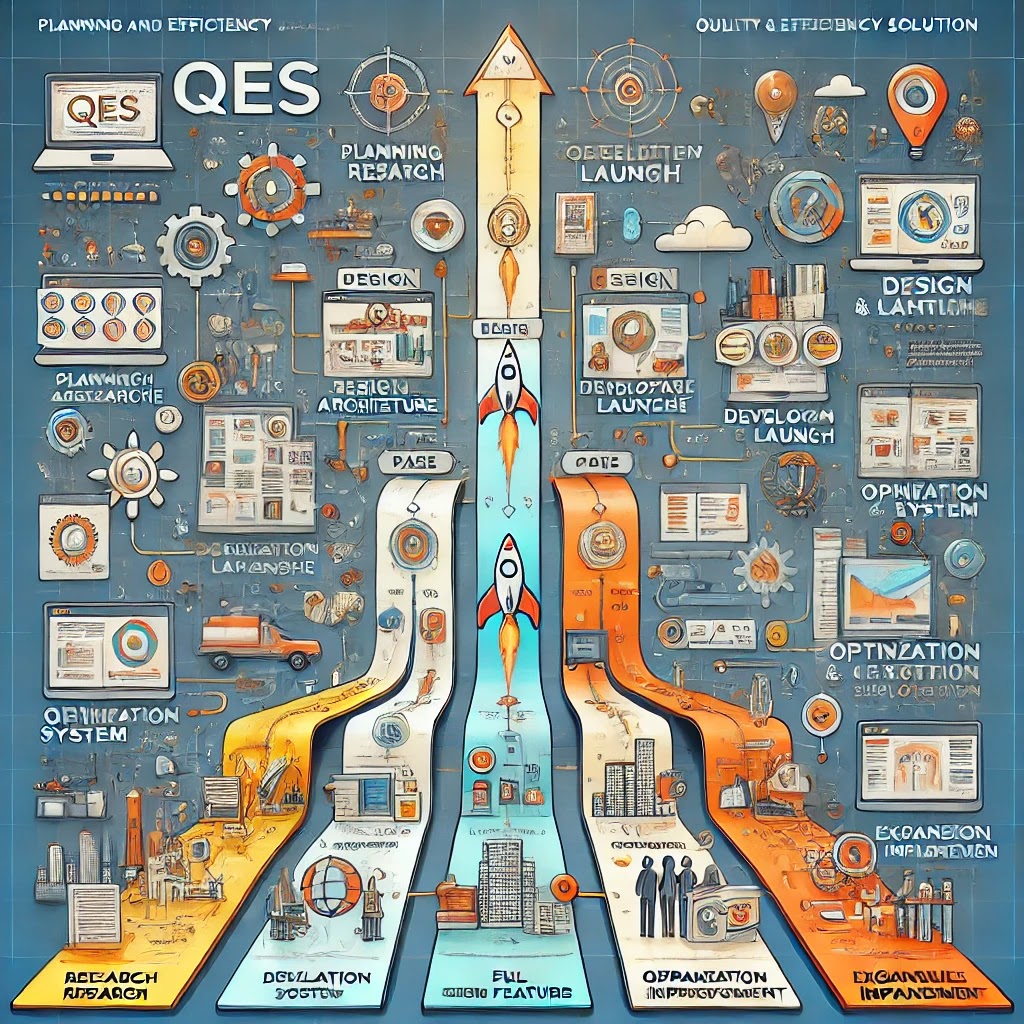
Phase 1: Planning and Research (0-3 Months)
Objectives:
- Identify key business needs related to quality and efficiency.
- Research existing solutions in the market and evaluate gaps.
- Collaborate with key stakeholders to outline core functionalities of QES.
Key Milestones:
- Market Research Report.
- Stakeholder Requirements Gathering.
- Product Requirement Document (PRD) Drafting.
Phase 2: Design and Architecture (3-6 Months)
Objectives:
- Finalize system architecture for QES.
- Define user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) requirements.
- Develop data models, workflows, and integration points with existing systems.
Key Milestones:
- Finalized System Architecture.
- User Interface (UI) Design Prototypes.
- Data Model Diagrams & Workflows.
Capabilities:
- Establishment of core modules for data input, analysis, and reporting.
- Initial integration with existing ERP and Quality Management Systems (QMS).
Phase 3: Development and MVP Launch (6-12 Months)
Objectives:
- Build the core modules for QES: Quality Assurance, Efficiency Tracking, and Process Optimization.
- Develop key features, including real-time analytics, reporting dashboards, and quality control automation.
- Launch the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) for select users.
Key Milestones:
- Core Feature Development (Quality Module, Efficiency Module).
- Completion of MVP Testing.
- MVP Release to Early Adopters.
Capabilities:
- Real-time Analytics: Users can monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate reports.
- Efficiency Tracking: Automated data collection and tracking of workflow efficiency.
- Quality Assurance: Implementation of QA checks and triggers for potential quality issues.
Phase 4: Full System Deployment (12-18 Months)
Objectives:
- Roll out the full version of QES to all users.
- Provide extensive training and support.
- Begin capturing feedback from users to improve functionality and ease of use.
Key Milestones:
- Full System Rollout.
- User Training Programs.
- Feedback Collection and Initial System Improvements.
Capabilities:
- Data Integration: Full integration with third-party tools (e.g., CRM, ERP).
- Custom Reporting: Ability to generate custom reports based on user preferences.
- Automated Alerts: Automatic notifications for quality issues or workflow inefficiencies.
Phase 5: Optimization and Advanced Features (18-24 Months)
Objectives:
- Focus on optimizing system performance and user experience.
- Introduce advanced analytics using AI and Machine Learning.
- Expand reporting capabilities with predictive and prescriptive insights.
Key Milestones:
- Performance Enhancements.
- Introduction of AI-driven insights.
- Predictive Analytics Deployment.
Capabilities:
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Utilize past data to predict quality issues and recommend efficiency improvements.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Provide actionable insights for optimizing processes based on real-time data.
- Enhanced Automation: Increased automation in workflows to reduce manual intervention.
Phase 6: Expansion and Continuous Improvement (24+ Months)
Objectives:
- Scale QES to support multi-industry use cases.
- Expand features to support industry-specific needs and compliance requirements.
- Continuously improve the system based on user feedback and evolving business requirements.
Key Milestones:
- Industry-Specific Feature Development.
- Expansion to Global Markets.
- Ongoing System Updates and Upgrades.
Capabilities:
- Scalability: Adapt QES for various industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
- Compliance Support: Ensure QES supports relevant regulations and standards (ISO, Six Sigma, etc.).
- Ongoing Development: Regular feature updates and performance improvements.
Summary of Core Capabilities:
Quality Management Module:
- Real-time monitoring of quality KPIs.
- Automated quality control triggers.
- Audit trail for quality-related issues.
Efficiency Optimization Module:
- Workflow tracking and bottleneck identification.
- Data-driven recommendations for process improvement.
- Automated reporting of efficiency metrics.
Predictive Analytics & AI Integration:
- Predict quality control failures and suggest preventive measures.
- AI-driven insights for optimizing efficiency across multiple departments.
Comprehensive Reporting:
- Customizable dashboards and detailed reports.
- Alerts and notifications for both efficiency gaps and quality risks.
Integration & Scalability:
- Seamless integration with ERP, CRM, and other business tools.
- Adaptable for different industries and scalable for global use.
Long-term Vision:
- Global Expansion: Position QES as a leading solution for global enterprises seeking to streamline operations.
- Industry Leader: Set the benchmark for quality and efficiency management across diverse industries.
- AI-driven Continuous Improvement: Utilize artificial intelligence to not only predict but also improve and optimize workflows without manual intervention.
This roadmap outlines the strategic direction and timeline for developing and enhancing QES. Each phase is designed to build on the previous, ensuring continuous improvement and integration of new features based on market and user needs.

.%20The%20diagram%20should%20include%20a%20central%20circle%20labeled%20'QES%20(Q.webp)
No comments:
Post a Comment